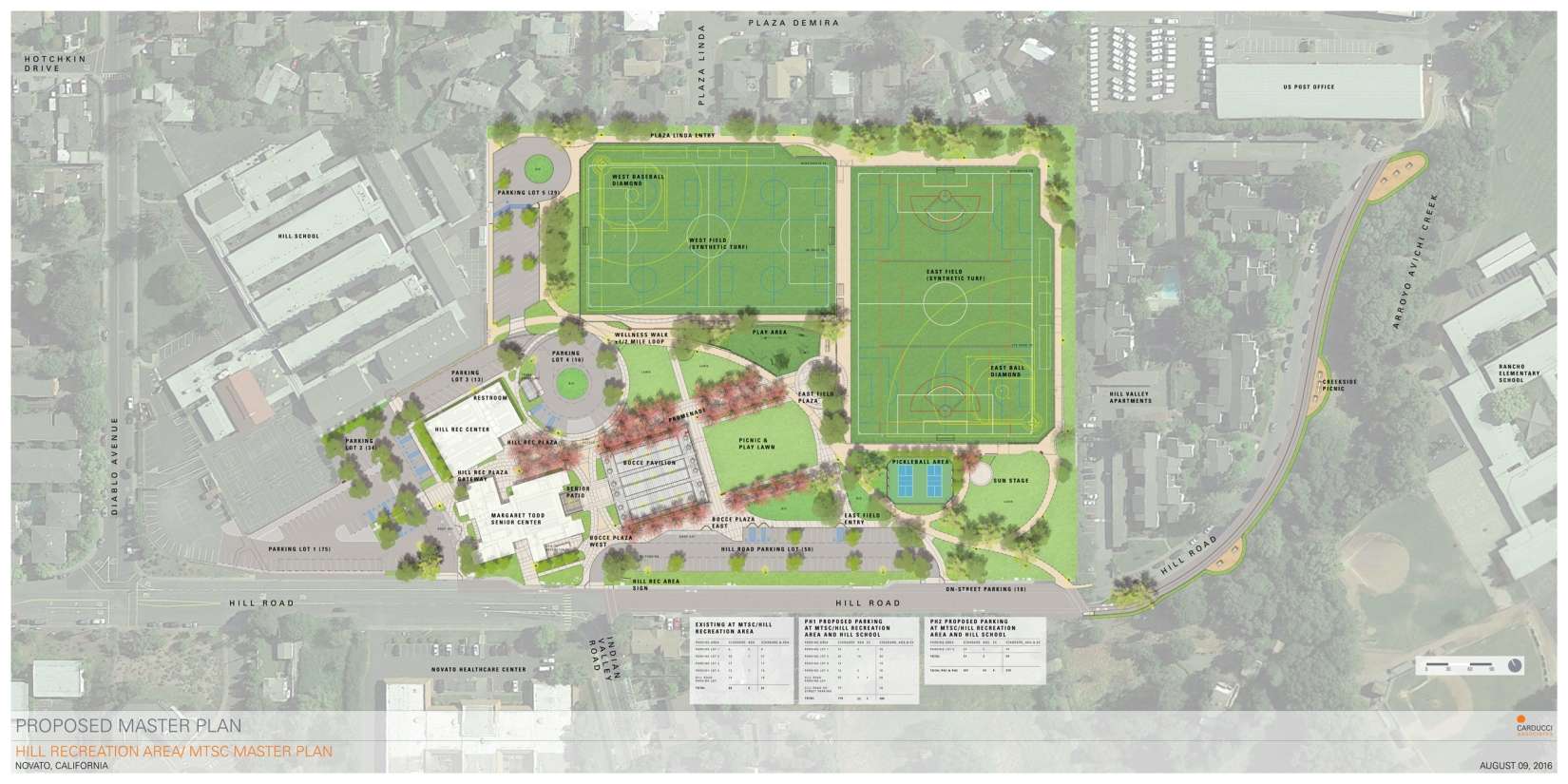
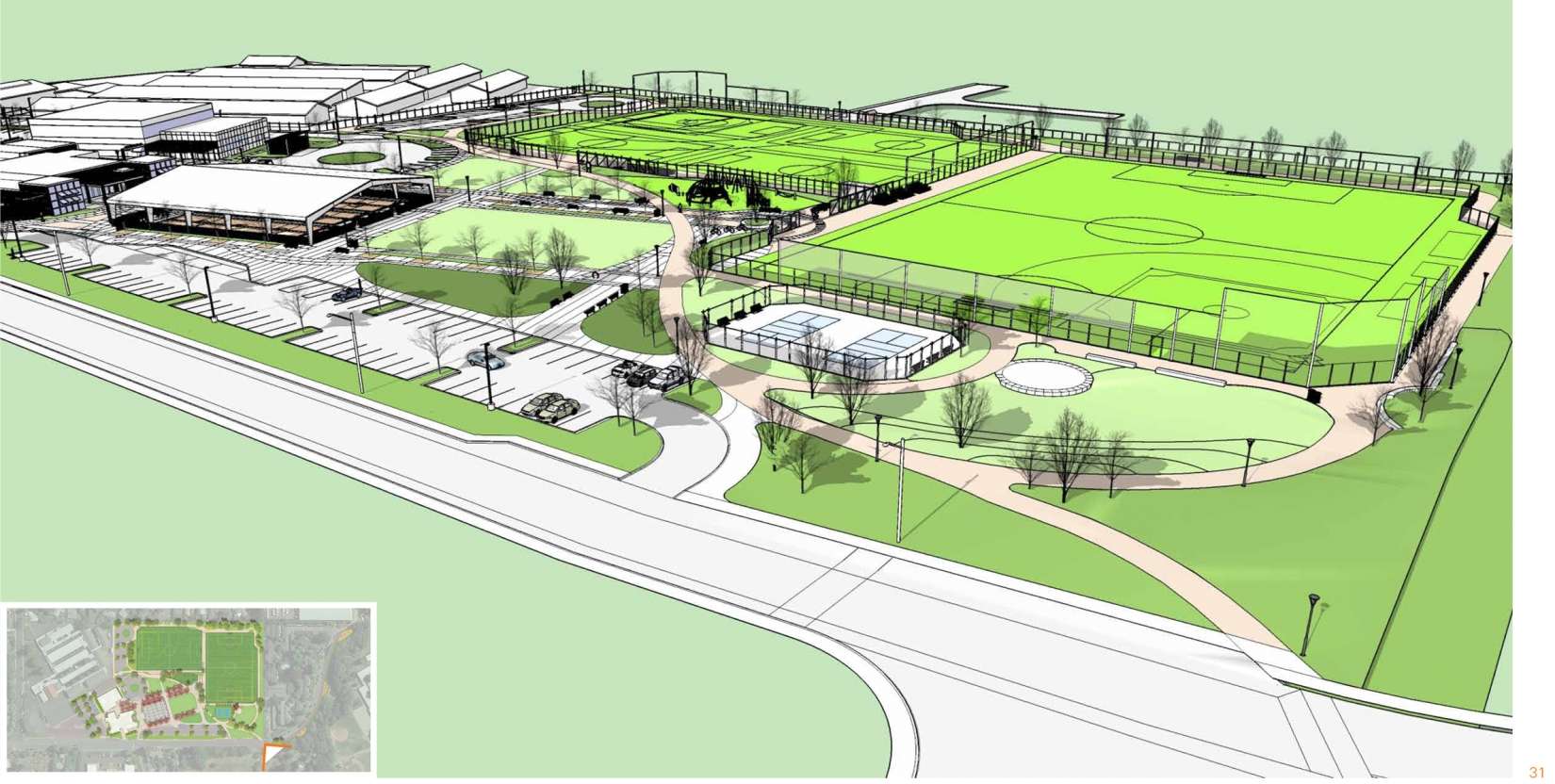
Contested Turf in San Francisco Bay Area Sports Field Design / Designing for Synthetic Turf Fields
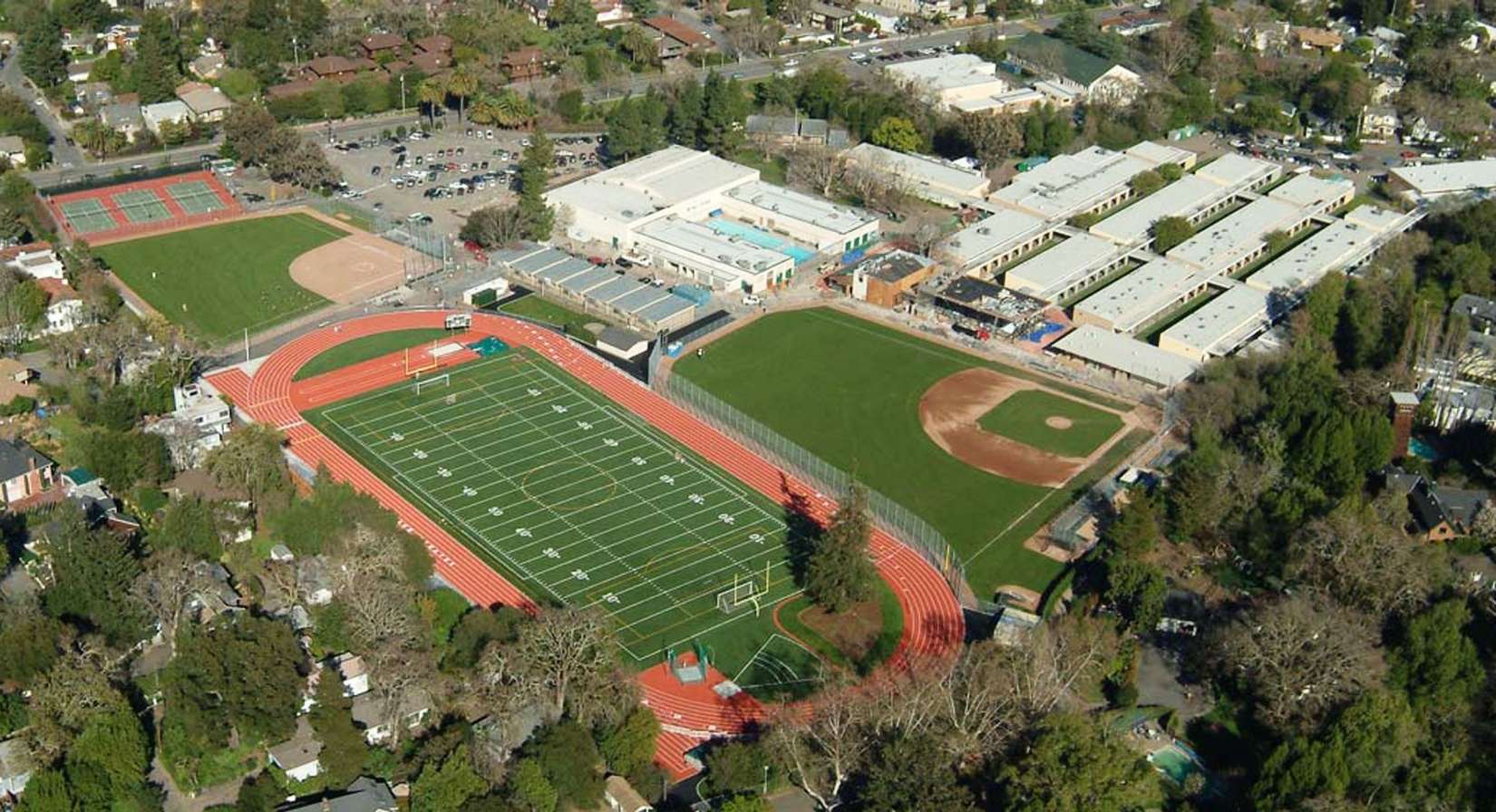
Sports fields provide a surprisingly complex terrain for landscape architects. Multi-use athletic fields ground significant contemporary themes in landscape architecture’s professional and academic worlds: the duality of the natural and the artificial, ecology as the protagonist of a design, and the unsung role of maintenance. Conversations during their site design process can play into a cultural aversion to material artifice or into the aesthetic preference for an evergreen lawn inherited from England.
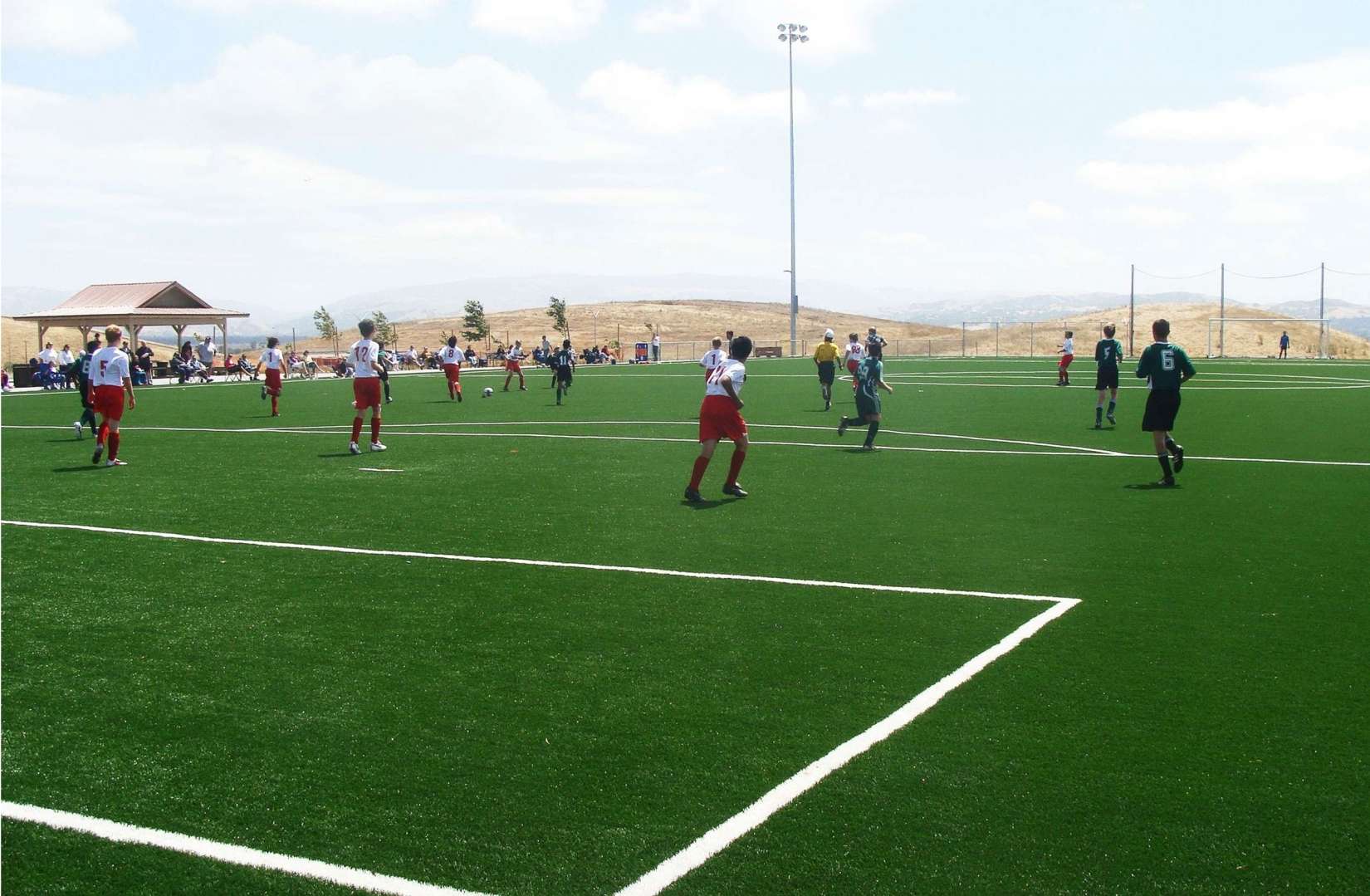
Benefits to Synthetic Turf Field Applications
The following land use, ecological, and athletic issues contribute to the growing use of synthetic turf:
- conflicting demands of natural turf for maintenance (which, like other biotic things, needs to breathe) and of a large population for play space in the expensive San Francisco Bay Area,
- shrinking maintenance budgets,
- creating a literal ‘even playing field,’ by avoiding soil’s lumpiness and grading for drainage, and
- growing public demand for low-water, drought-resilient landscapes.
Evolving Scientific Research and Site Design
But a synthetic turf sports field also raises emotionally-charged concern over its impact on the environment and on health and safety of athletes, especially children.
On public projects, landscape architects are caught in between those convinced synthetic turf is harmful and those convinced synthetic turf is safe, each citing different studies. Anticipating this challenge, Carducci Associates mediates between the diverse priorities of public field users, scientific findings, and clients. Bringing scientists, with expertise in the material components of synthetic turf and in research processes, into design and public processes helps.
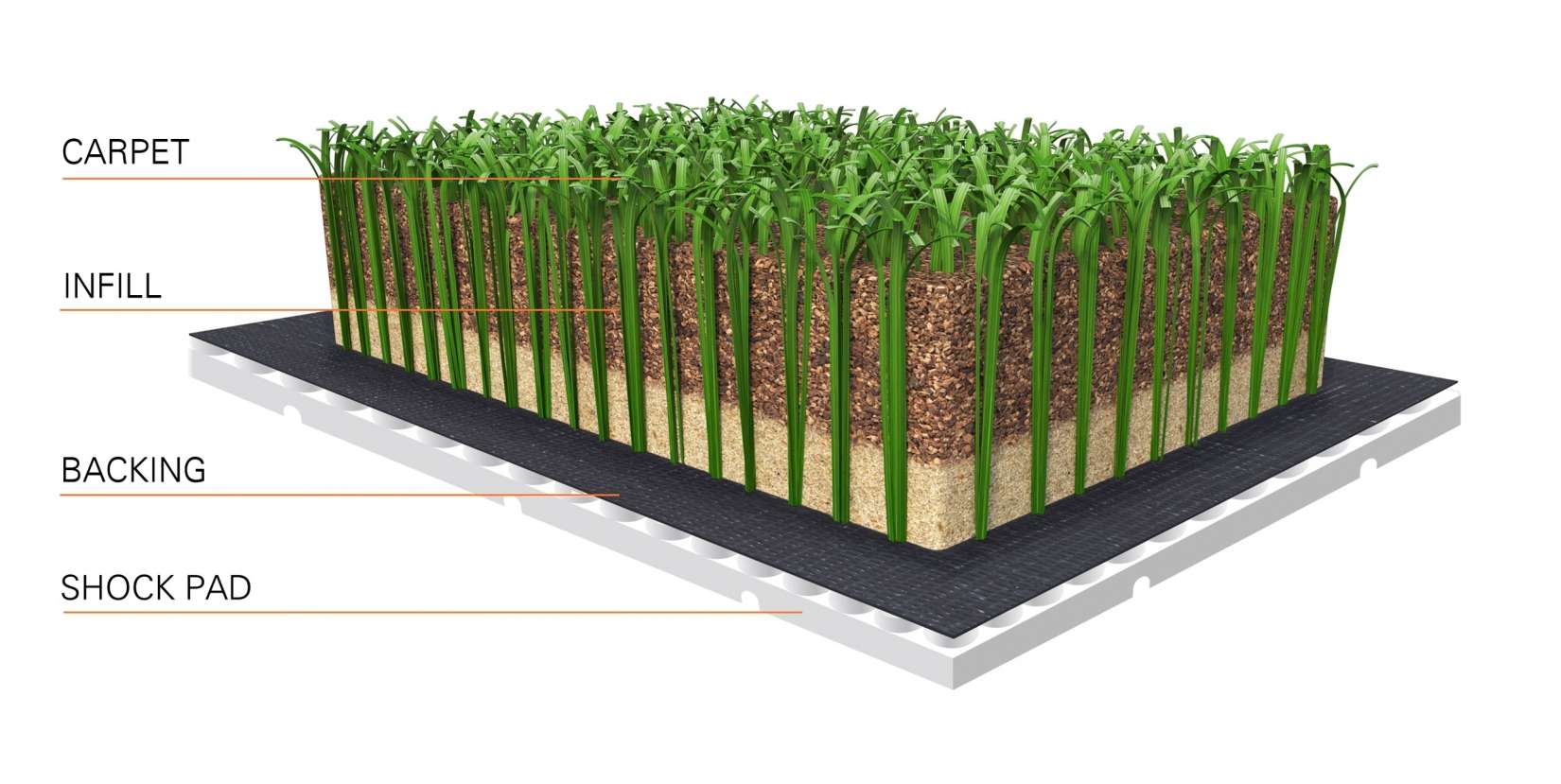
Within the nuanced process of designing a synthetic turf field, infill has become one of the most controversial components. A granular material that works as a synthetic stand-in for soil, infill is often comprised of crumbled, recycled rubber tires. Crumb rubber has raised concerns nationally and locally, from a recent artificial turf installation at the Beach Chalet Fields in San Francisco’s Golden Gate Park, to a multi-agency federal initiative launched in February 2016 known as the Federal Research Action Plan on Recycled Tire Crumb Use on Playing Fields and Playgrounds. In June 2015, the California Environmental Protection Agency the Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA) committed under a contract with CalRecycle to conduct a new study on synthetic turf and potential human health impacts.
While crumb rubber is under scrutiny, user groups are calling for infill alternatives that contain materials like recycled athletic shoes, cork and coconut, or other synthetic materials. The Los Angeles Unified School District and the New York City Department of Parks and Recreation no longer use crumb rubber. In the greater San Francisco Bay Area, dozens of facilities (including schools, public parks, the Facebook Corporate Campus) have used infill alternatives fabricated with cork, organic fiber, recycled turf, sand and TPE (a plastic).
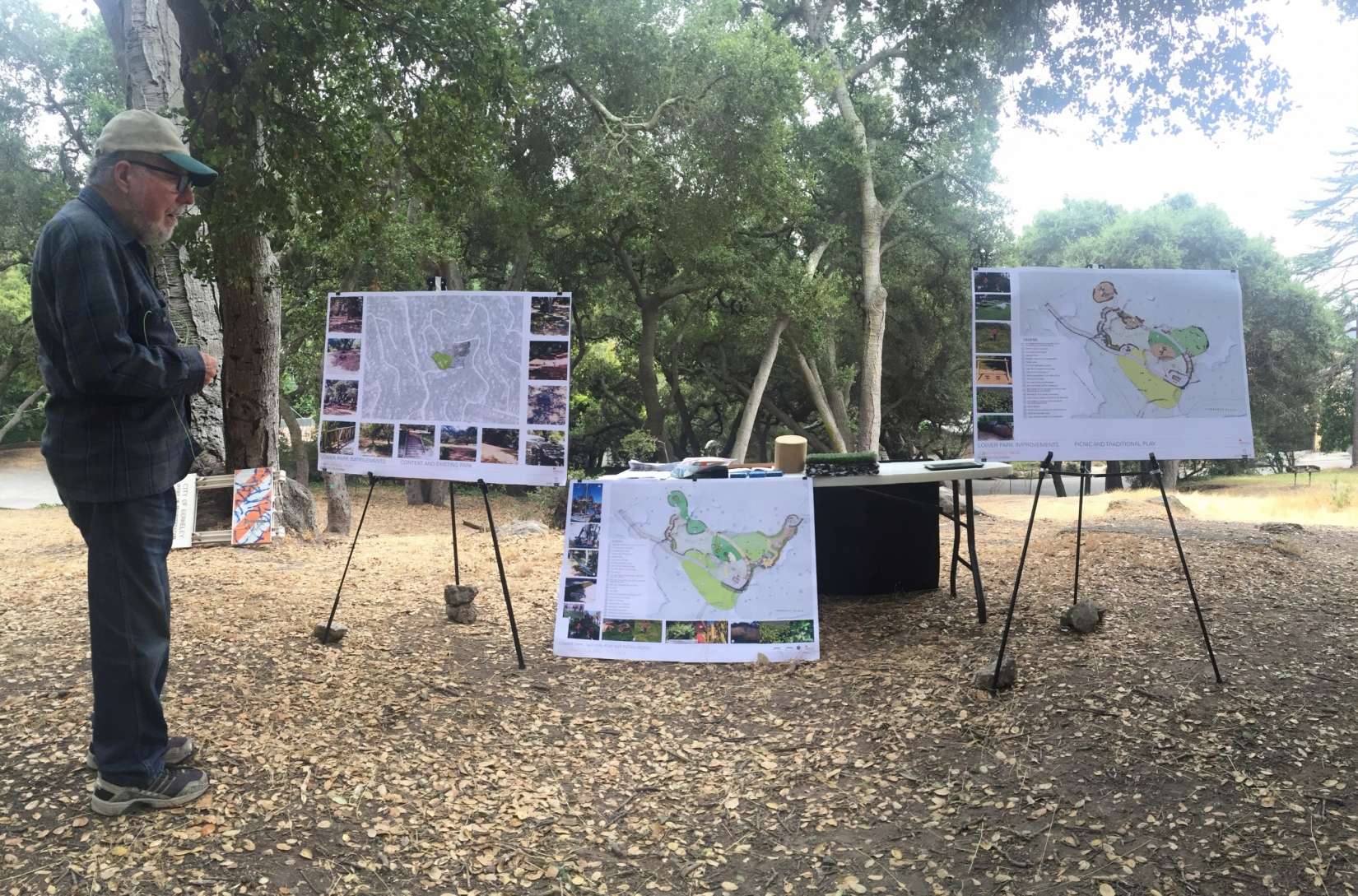
Carducci Associates’ Leadership in Sports Field Design
For community meetings, Carducci Associates has analyzed more than a dozen synthetic turf infill materials with its team of experts: Principals Bill Fee and Vince Lattanzio, Associate Principal Wesley Bexton, Senior Associate Alvin Tang, and Associate Philip Dinh (bios here). While comparing playability, cost, material components, and maintenance, alongside a timeline of political, funding, and construction processes, we record and respond to public questions and concerns. Attendees’ priorities at recent community meetings focus on long-term ecological, economic and health concerns:
1. Install a non-crumb rubber field that allows for healthy recreation.
2. Study the lifecycle costs of crumb rubber and alternatives, beyond capital cost, to address disposal and longevity.
3. Consider phasing strategies that permit for more expensive alternative infills.
4. Cost is less of a priority than health and safety.
The results of current federal and state studies on crumb rubber infill have yet to surface in part because the health impacts of exposure will be studied during the hottest months of 2017. While agencies, designers and athletes wait for the outcome, landscape architects should study and incorporate the research findings that are available on crumb rubber and alternative infills, and engage in outreach and discussion with athletes, coaches and families on their preferences for and experiences with synthetic turf fields and different infill.
References
California Environmental Protection Agency Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, “Synthetic Turf Studies,” last modified March 9, 2017, https://oehha.ca.gov/risk-assessment/synthetic-turf-studies.
Gutierrez, Melody, “US to mount multiagency study of health risks of synthetic turf,” San Francisco Chronicle, February 12, 2016, http://www.sfgate.com/nation/article/US-to-mount-multiagency-study-of-health-risks-of-6827632.php
United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Federal Research on Recycle Tire Crumb Used on Playing Fields,” last modified December 30, 2016, https://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/federal-research-recycled-tire-crumb-used-playing-fields.